Intelligent Lakehouse: The Future of Data & AI
In today’s data-driven era, acquiring the right data, ensuring quality, and governing it effectively are essential for organizational success. Failure to do so can mean losing significant business opportunities. This article demonstrates how the Lakehouse architecture enables organizations to harness data strategically and unlock its true value.
This Article talks about “Intelligent Lakehouse: The Future of Data & AI”. We will highlight different components of the diagram in the Article below:
Internal Applications: Enterprise has its own set of applications (based on business Domain), from Web applications, Databases, ERP, CRM, mobile apps, etc.
External Applications: In many cases, enterprises need not manage every application in-house. Required functionalities can be acquired externally, with the complete ecosystem supported and maintained by third-party vendors.
Integration Layer: Bringing data from Internal or External Applications falls in the purview of the Integration Layer. This data will flow in the form of Files, API, or streaming.
Lakehouse: Stores all types of data (structured, semi-structured, unstructured, streaming) like a data lake. We can create a raw, model, and aggregated layer out of it.
Data Quality: High-quality data is a critical dimension of any data-driven system. Incomplete or inconsistent data can lead to misleading insights. Therefore, it is essential to build or adopt a robust data quality framework to ensure accuracy and trust in analytics.
Data Governance: Data Governance is the framework of policies, processes, roles, standards, and technologies that ensures an organization’s data is accurate, consistent, secure, and used responsibly.
Data Security: Data should be secure from misuse, threats, and unauthorized access.
Semantic Layer: A Semantic Layer is a business-friendly abstraction layer that sits between raw data sources and end-user tools (BI dashboards, AI models, applications).
Analytics: From the aggregate layer, we can expose data to reporting tools such as Power BI, Tableau, Looker, etc.
Customer Data Platform: A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a centralized software system that collects, unifies, and manages customer data from multiple sources to create a single, consistent, and comprehensive customer profile.
Advance Analytics: We can create forecasting reports using the Machine learning capabilities. Thease are a wide range of reports such as Inventory forecasting, sales forecasting, customer churn, etc.
Summary:
A well-designed Lakehouse unlocks the true potential of enterprise data, delivering actionable insights that drive new initiatives and accelerate revenue growth. By unifying structured and unstructured data under a single architecture, it eliminates silos and ensures faster access to trusted information. This modern approach not only reduces complexity and cost but also empowers business leaders to innovate with confidence, improve customer experiences, and make data-driven decisions at scale. Ultimately, the Lakehouse becomes the foundation for sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the digital era.
Security Layers for Enterprise LLM-Based Applications
In the era of Large language model (LLM) availability and their uses, enterprise has to be careful to design their applications, considering external threat and attacks. We have been discussing some of the best practices to enable security for LLM-based applications at the Enterprise level. There are a bunch of tools in the market; however, our article focuses more on the method instead of Tools, as we have proposed the following layers of security, which include traditional methods and new, evolving methods. More details are given below:
API Gateway:
User-initiated traffic passes through the API gateway. We have to implement authorization and authentication. Additionally, we can leverage the API gateway for the following services:
1. Auth & RBAC
2. Rate Limiting
3. WAF & Bot Protection
4. TLS + GW level Logging
AI Gateway:
The next component is the AI Gateway, which can scan both incoming and outgoing traffic. It can perform the following things:
1. PII/PHI Protection
2. Prompt Security
3. Output Guardrails
4. Audit & Compliance
Application or Code level:
For a genAI application, we can build an additional framework, which can add functionality to sanitize incoming text. This new table will contain the metadata for sensitive information, prompts, jailbreak text, and other elements used for validation. Text will be sensitized before sending to LLM. Similarly, outgoing text will also be sanitized at the application level.
Database:
The database is an important component; we can't expose enterprise data to everyone. Here comes role based, ABAC, column/ row level security, other than encrypting data.
Summary:
leveraging API/AI Gateway, code level data sanitization and enabling data security and governance principal, we can make safe and better AI application.
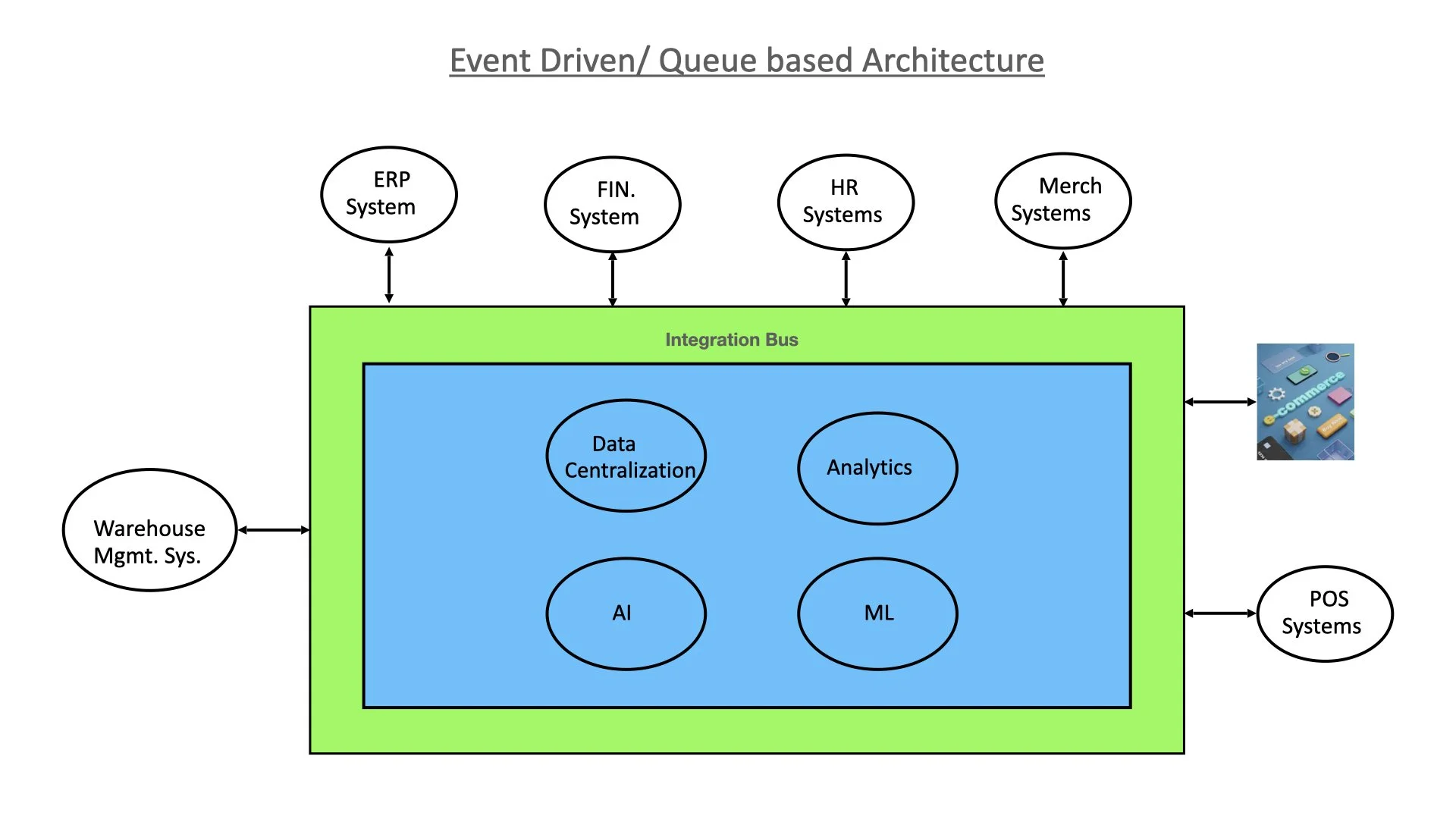
Event-Driven / Queue-Based Architecture in Retail
Introduction
Retail organizations today operate in highly dynamic environments where real-time responsiveness is critical. Whether it’s inventory updates, customer orders, fraud detection, or personalized marketing, the ability to process and respond to events as they occur can directly impact revenue and customer satisfaction. This is where Event-Driven Architecture (EDA) and Queue-Based Systems come into play.
What is Event-Driven Architecture?
Event-Driven Architecture is a design paradigm where events (such as “order placed,” “item shipped,”) act as the primary communication mechanism between services. Instead of polling or requesting data continuously, services subscribe to and react to events as they happen.
In a retail context:
A customer order generates an event.
The inventory service consumes the event and reduces stock levels.
The billing service processes payment.
The shipping service schedules delivery.
The marketing service may trigger loyalty rewards or personalized offers.
Role of Queues in Retail
While events are asynchronous, queues ensure reliability and order:
Message Queues (e.g., Kafka, RabbitMQ, AWS SQS, Azure Service Bus) store events until consumers process them.
This prevents data loss during traffic spikes (e.g., Black Friday sales).
Multiple consumers can subscribe, ensuring parallel processing across retail functions.
Benefits for Retail Companies
Scalability – Handle millions of orders, product updates, and customer interactions in peak shopping times without downtime.
Resilience – If one microservice (e.g., shipping) is down, events remain in the queue until it recovers.
Real-Time Experience – Customers see real-time stock availability and order confirmations.
Decoupling – Services like payment, inventory, marketing, and logistics evolve independently.
Data-Driven Insights – Streaming data pipelines provide customer behavior analytics in real-time.
High-Level Architecture Diagram
Conclusion
Event-Driven and Queue-Based Architecture enables modern retail companies to transform from batch-driven, siloed systems into real-time, scalable, and customer-centric ecosystems. With careful implementation, retailers gain agility to react instantly to customer needs, optimize operations, and innovate faster in a highly competitive market.
Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol
Introduction:
The rapid advancement of AI has ushered in a new era of intelligent systems, where autonomous agents are no longer just experimental but are being deployed at scale across industries. As these agents grow in complexity and number, seamless communication between them becomes essential. To address this, Google introduced the Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol—a structured approach designed to facilitate efficient, reliable, and standardized communication among AI agents.
This protocol emerges as part of the broader evolution in AI infrastructure, where new processes and frameworks are continuously being developed to meet real-world demands. A2A enables agents to collaborate, delegate tasks, and share context—paving the way for more advanced, multi-agent systems capable of solving complex problems in dynamic environments.
Approach:
Fig.1. A2A Flow
As illustrated in the diagram, the user initiates a request through an application. The application forwards this request to an intelligent agent (Agent 1). During processing, Agent 1 identifies the need for additional context or data that it does not possess. Instead of redundantly fetching or recalculating the information, Agent 1 communicates with another agent (Agent 2) that already holds the required knowledge. By leveraging Agent 2’s capabilities via the Agent2Agent (A2A) Protocol, Agent 1 can quickly access the necessary data, respond more efficiently, and significantly reduce processing time and resource consumption.
Benefits:
Discovery:
Agents can dynamically identify and locate other agents with the necessary capabilities or data. This enables more flexible and scalable multi-agent ecosystems.
Negotiation:
Agents can communicate to reach agreements on how to share resources or divide tasks. This promotes efficient and autonomous decision-making in distributed systems.
Task Management:
A2A allows agents to delegate, accept, or coordinate tasks based on their availability and specialization. This ensures optimal task distribution and load balancing.
Collaboration:
Agents can work together by exchanging context, insights, and progress updates in real-time. This leads to more intelligent, cooperative behavior across complex workflows.
References:
https://developers.googleblog.com/en/a2a-a-new-era-of-agent-interoperability/
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-cloud/blog/2025/05/07/empowering-multi-agent-apps-with-the-open-agent2agent-a2a-protocol/
Part 1: Exploring Model Context Protocol (MCP) in Data and AI
Introduction:
AI is not new to us; over time, enormous studies and research have been conducted in this area. Whether it is machine learning, Deep learning, expert systems, Robotics, Image, or Natural language processing, all these AI subfields went through significant changes; however, December 2022 was a watershed moment for Deep learning. During this time, OpenAI [2] introduced the LLM model. Not only the industries, but even the common man has started using the LLM [1]. We have seen chatbots and other use cases floated around using LLM. LLMs are good for text summarization, but can’t store data and talk to applications. Let's say LLM has written an email, but it does not know whether this email has to be sent through Gmail or Outlook. Industry was missing a kind of standard. At the end of 2024, anthropic Team [3][4] has launched a defined standard on how LLM can be leveraged within the industry or outside of the industry (how tools and systems can feed structured data into LLM). It has given more opportunities to use LLM in subsequent use cases and a better method of interaction with applications.
Details Discussion:
As per the diagram, the user query is received by the application or program, which will have capabilities to connect with different systems such as databases, web applications, and so on. As per Fig.1, the middle part will resolve the context and will send this to the LLM model for the subsequent task, and will get a response from the LLM. Based on the logic, in case a program or app connects to the required applications.
Experiment:
from mcp.server import MCPServer
from pymongo import MongoClient
class MongoDBMCPServer(MCPServer):
def __init__(self, mongo_uri):
super().__init__()
self.client = MongoClient(mongo_uri)
self.db = self.client.your_database_name
# Registering a tool to find documents
self.register_tool("find_documents", self._find_documents)
def _find_documents(self, collection_name, query):
collection = self.db[collection_name]
results = list(collection.find(query))
return {"status": "success", "data": results}
# Example usage:
# server = MongoDBMCPServer("mongodb://localhost:27017/")
# server.run() # This would start the MCP server
server.operation({ …
});
server.operation({
name: “insertDocument”,
description: “Insert a document into a mongoDB collection”,
input: InsertDocumentSchema,
….
});
server.operation({ …
});
server.operation({ …
});
// Initialize the server
const.transport = new StdioServerTransport();
server.listen(transport)
There are numerous places where we can use MCP in Data and AI areas, a few examples are given below:
1. Getting a pipeline (e.g., ETL) job failure reason
2. Which dataset failed the quality check, and why?
3. Sales report execution
4. Sales forecasting
Summary:
Model context protocol has paved the way to acquire companies and build a variety of use cases using Large Language Model (LLM). It has simplified the work and increased productivity within the industry.
References:
[1]. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Large_language_model&action=history, 0:24, 3 August 2025
[2]. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenAI
[3]. https://blog.modelcontextprotocol.io/posts/welcome-to-mcp-blog/
[4]. https://modelcontextprotocol.io/overview
Revolutionizing Data-Driven Enterprises with Large Language Models (LLMs)
Introduction: The Data-First World We Live In
Explosion of Data from Modern Technologies
We live in an era where data isn’t just being generated — it’s erupting like a digital volcano. Web applications, mobile apps, social media, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT devices are spewing out torrents of information every second. Whether it’s a drone mapping a city, a fitness tracker recording steps, or an e-commerce app capturing clickstreams, the outcome is the same: enormous volumes of data, captured at breakneck speed and with varying structures.
What’s truly groundbreaking is not just the volume, but the velocity and variety. It’s no longer just structured data from databases but unstructured formats like videos, audio logs, emails, and sensor data. Healthcare systems, for instance, are flooded with MRI scans, patient records, prescriptions, and clinical trial results — all of which hold critical insights, if only we could tap into them quickly.
The Role of Enterprises in Extracting Value
Enterprises today are sitting on a goldmine of data. Yet, merely having access to data is no longer a competitive edge. The real differentiator is in extracting actionable insights — quickly and efficiently. Data analytics has traditionally required a well-oiled machine of data engineers, analysts, and domain experts. This machine, while effective, is time-consuming and expensive. The process of collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data can span weeks to months, depending on complexity.
Executives and decision-makers often find themselves waiting for dashboards or custom reports to make strategic decisions. And in today’s fast-paced world, delay equals lost opportunities. Businesses need answers in hours — not weeks.
The Promise of Large Language Models (LLMs)
This is where Large Language Models (LLMs) [1] enter the scene. Think of them as intelligent assistants trained on massive corpora of text and data, capable of understanding human language and context. But they’re not just glorified chatbots. LLMs can generate code, write SQL queries, summarize documents, and even conduct preliminary data science tasks — all through simple natural language commands.
The implications for enterprises are profound. With LLMs, the barriers to accessing and interpreting data crumble. Non-technical stakeholders can ask business questions in plain English and receive answers that previously required specialized teams to provide. The result? More people making data-driven decisions, faster turnaround times, and a significant boost in business agility.
Understanding LLMs and Their Business Relevance
What Are Large Language Models?
Large Language Models are AI systems trained to predict and generate human-like text. They’re built on transformer architecture, which allows them to analyze context across large bodies of text and produce coherent responses. The most famous examples include OpenAI’s GPT models, Google’s PaLM, and Meta’s LLaMA.
They are trained on diverse datasets — ranging from books, research papers, blogs, to programming documentation. This equips them with a generalized understanding of language, logic, code, and even reasoning. The best part? They can be fine-tuned to suit domain-specific needs — be it finance, healthcare, or manufacturing.
How LLMs Fit into Enterprise Data Strategy
Most enterprises have invested in a data ecosystem comprising databases, analytics platforms, business intelligence (BI) tools, and data lakes. But these systems are fragmented and require technical proficiency to extract insights.
LLMs can be integrated into this ecosystem to act as a bridge between humans and data. They can query data warehouses using natural language, explain data trends in plain terms, and automate repetitive reporting tasks. Think of it as embedding a highly skilled data analyst within every application — always available and infinitely scalable.
Efficiency Gains from LLMs
The key advantage of LLMs isn’t just intelligence — it’s speed. What used to take hours of SQL writing or data wrangling can now be accomplished with a sentence. A sales manager might say, “Show me the top 10 products by revenue in Q1 2024,” and get a detailed report instantly.
LLMs also reduce dependency on specialized roles for routine analysis, freeing up technical teams to focus on innovation rather than operational tasks. This doesn’t mean jobs are being replaced; rather, human potential is being reallocated to higher-value initiatives.
Use Case 1: LLMs for SQL Report Generation
The Traditional Workflow of Report Creation
In most organizations, report generation is a multi-step affair. It typically begins with a request from an executive or business stakeholder. This request travels through multiple teams — analysts to understand requirements, data engineers to build ETL pipelines, and BI developers to visualize the data. Depending on complexity, this process can stretch from a few days to several weeks.
Moreover, each change or follow-up request restarts the cycle. If the executive wants to slice the data by geography or adjust metrics, the entire pipeline may need tweaking. This dependency chain is inefficient, costly, and hinders agility.
Barriers Faced by Non-Technical Users
One major roadblock is language. Most executives don’t speak SQL or Python. And why should they? Their expertise lies in strategic thinking, not query optimization. Yet, in the traditional model, their insights are bottlenecked by their inability to “speak” to the data systems directly.
This creates a divide — those who can access data (technical teams), and those who need data to make decisions (business users). This misalignment often results in delayed insights, lost context, and missed opportunities.
How LLMs Simplify Report Generation
With LLMs, that divide is eliminated. These models can interpret natural language queries and convert them into SQL statements or even call APIs to fetch data. For instance, a simple prompt like “Show monthly sales trends for the North American region” is translated into a SQL query and run on a Snowflake or BigQuery backend.
But it’s not just about syntax translation. LLMs understand business context. They can infer what “sales trends” means, which tables to query, and how to group data over time. This makes them powerful allies in generating fast, reliable, and contextual reports.
Example: Sales Forecasting via Natural Language Prompting
Consider a scenario where a company needs a sales forecasting report for the next quarter. Traditionally, this involves gathering historical sales data, cleaning it, selecting a model, training it, and finally visualizing the output — a process that can take months.
With LLMs, a business user can simply ask, “Forecast next quarter’s sales using last year’s data and account for seasonality.” The LLM will fetch historical data, apply a time series model (like ARIMA or Prophet), and present predictions — sometimes even visualized.
This drastically reduces the time-to-insight, lowers costs, and empowers decision-makers with timely, actionable intelligence.
Summary: The Future of Enterprise Intelligence
As data continues to grow at exponential rates, the challenge for enterprises is no longer in acquiring it — but in making sense of it quickly and efficiently. Large Language Models (LLMs) are redefining how we interact with data by bridging the gap between natural language and technical data systems. Through practical use cases like automated SQL report generation and accelerated data science workflows, LLMs are enabling faster, democratized, and more accessible insights across organizations.
This doesn’t imply that human roles will vanish. Instead, these technologies enhance human capabilities, allowing technical teams to focus on strategic innovations while enabling non-technical users to self-serve their data needs. From reduced costs and shorter timelines to smarter, faster decision-making — LLMs are rapidly becoming a cornerstone in enterprise digital transformation.
Adopting LLMs isn’t about replacing the workforce; it’s about redefining how value is delivered across the organization. With tools like agents, LangChain, and prompt-based querying, businesses now have the opportunity to unlock the true potential of their data ecosystems, regardless of internal technical limitations.
Whether you’re an executive, data analyst, or part of an IT leadership team — it’s time to embrace LLMs as your strategic advantage in this data-driven era.
References
[1]https://medium.com/data-science-at-microsoft/how-large-language-models-work-91c362f5b78f
[2]https://medium.com/data-science/how-llms-will-democratize-exploratory-data-analysis-70e526e1cf1c
[3].https://stefanini.com/en/insights/articles/llm-data-assistants-will-improve-data-democratization